Why Proper Generator Installation Matters
Installing a generator means working directly with your home’s electrical and fuel systems — two areas where mistakes can have serious consequences. Improper wiring can damage appliances, overload circuits, or even send dangerous voltage back through utility lines. Poor placement can allow carbon monoxide to enter the home, and inadequate grounding or weather protection can shorten the unit’s lifespan.
A professional installation ensures your generator is safe, code-compliant, and ready to perform when you need it most. It also protects your investment by keeping manufacturer warranties intact, meeting local permitting requirements, and ensuring safety features like transfer switches and shut-off valves work as intended.
Common risks of improper generator installation include:
- Electrical hazards such as backfeeding power into utility lines, which can endanger utility workers.
- Carbon monoxide exposure if the generator is placed too close to doors, windows, or vents.
- Fire risks caused by faulty wiring or improper fuel connections.
- Voided warranties when manufacturer installation guidelines aren’t followed.
Professional installers are trained to follow the National Electrical Code (NEC) and local building requirements, helping ensure your system is safe, efficient, and fully compliant.

DIY vs. Professional Installation
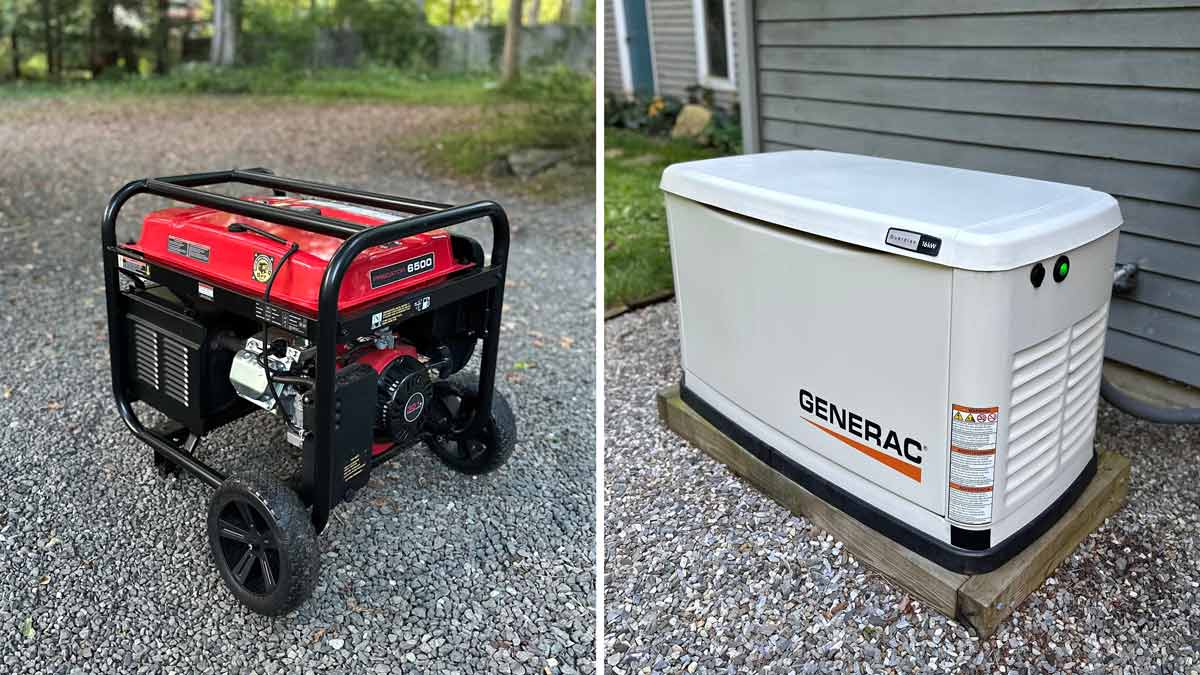
Can you install a generator yourself? It depends on the type of generator, how it connects to your home, and local regulations.
Portable generators that plug directly into appliances — or into a pre-installed inlet with a manual transfer switch — can often be set up safely by homeowners. These systems don’t require permanent wiring changes or fuel line modifications, making them more manageable for those comfortable with basic electrical safety.
Whole-home standby generators, however, are far more complex. They involve high-voltage wiring, integration with your electrical panel, and connection to a permanent fuel source. In most areas, permits, inspections, and licensed professionals are required to meet code and warranty standards.
» See Our Guide: Portable vs. Whole-House Generators
When DIY Can Work
- Running a few appliances with a portable generator and extension cords.
- Connecting a portable or inverter generator to a home circuit using a pre-installed manual transfer switch or approved interlock kit.
- Using generators without permanently wiring them into your home’s electrical system.
When to Call a Professional
- Installing a standby generator connected directly to your electrical panel.
- Adding or modifying natural gas, propane, or diesel fuel lines.
- Installing an automatic transfer switch.
- Any project requiring electrical or fuel permits and inspections.
Bottom Line
Standby generator installations involve complex wiring, fuel connections, and load calculations. Mistakes can lead to unsafe conditions, costly repairs, or system failure during an outage — making professional installation the safer choice.
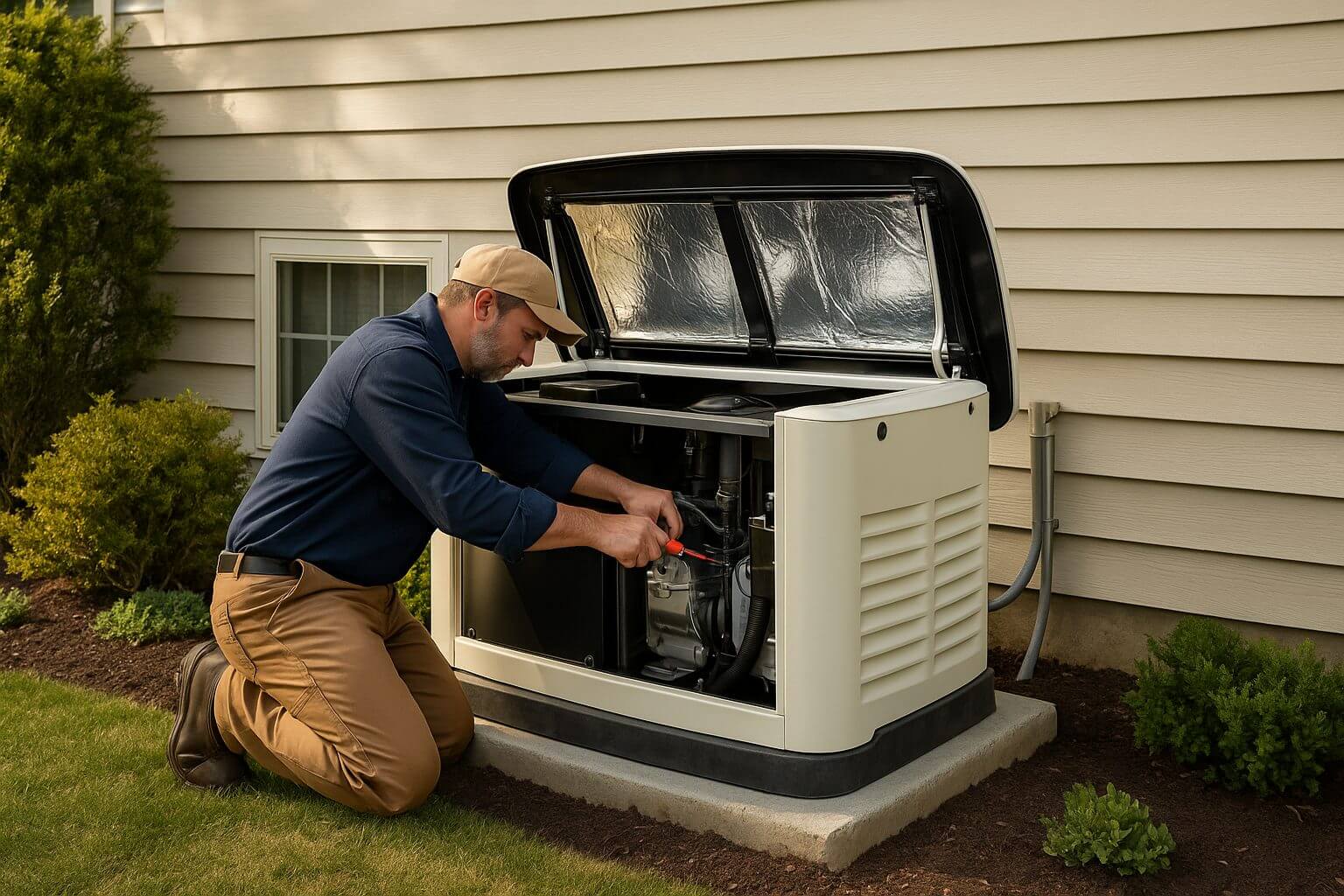
Step-by-Step: How a Professional Installs a Standby Generator
What does professional generator installation involve? It’s a multi-stage process that combines electrical work, fuel system setup, and code compliance.
While the exact steps vary by home and generator type, most professional installations follow the same core process to ensure safe, reliable operation.
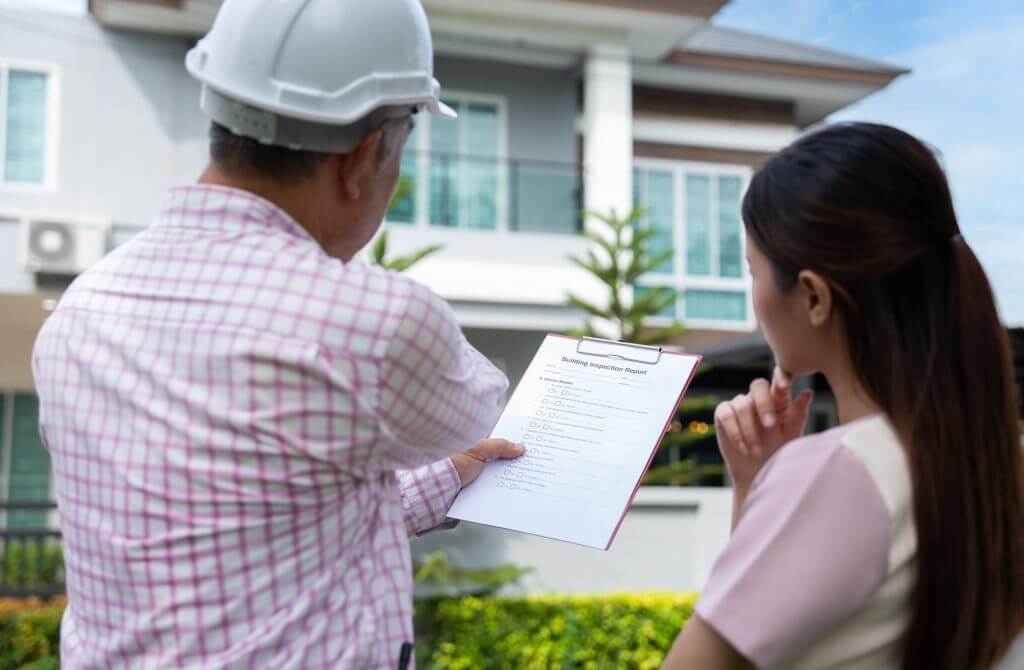
1. Site Assessment and Permitting
The installer evaluates your home’s electrical capacity, fuel options, and ideal generator location. They also handle required permits, which may include electrical, fuel, zoning, or HOA approvals.
- Evaluate electrical system, fuel source, and placement options.
- Obtain permits and approvals before work begins.

2. Selecting the Location
Generators must be placed on a stable, level surface with proper ventilation and clearance to prevent safety issues.
- Choose a level, well-ventilated location.
- Install on a concrete pad or compacted gravel base.
- Maintain at least 5 feet from openings and 18 inches from walls.
- Ensure easy access for maintenance.
3. Preparing the Site
Proper site preparation helps protect the generator from long-term damage caused by moisture or shifting ground.
- Level and compact the soil.
- Install the generator pad.
- Create drainage to prevent water pooling.
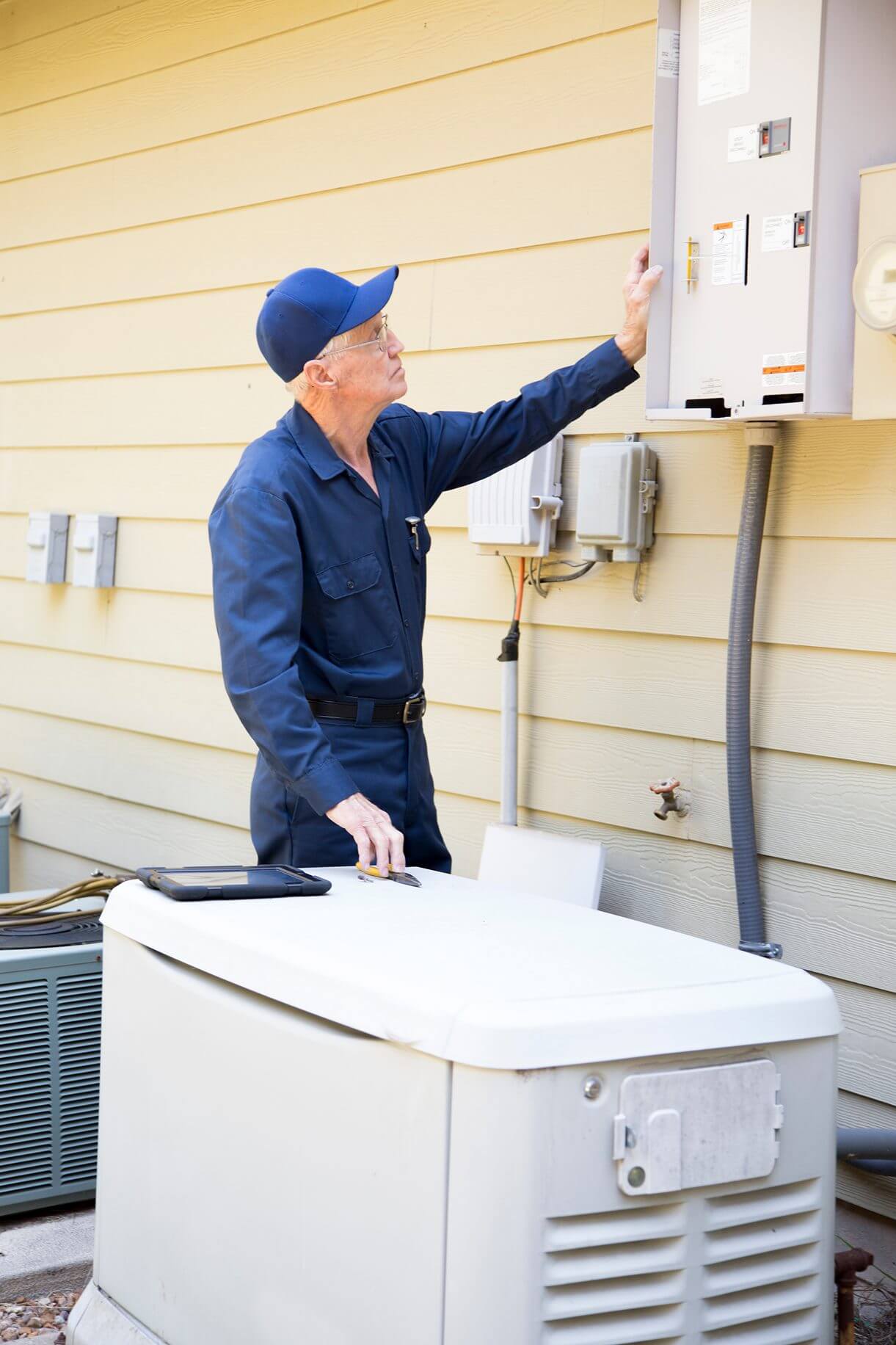
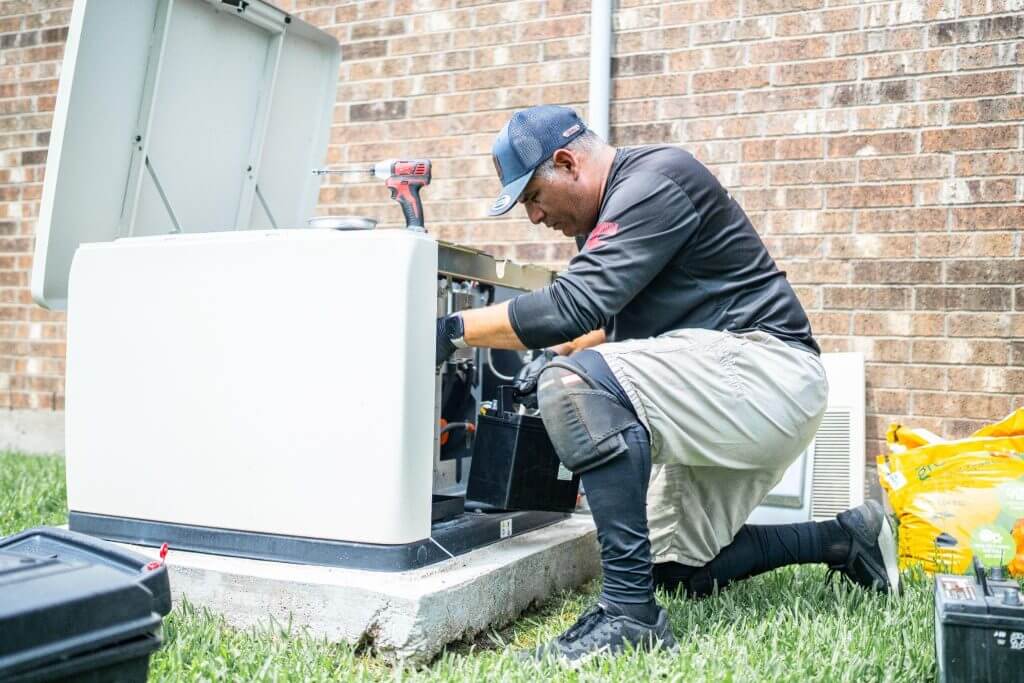
4. Electrical Connection
A transfer switch safely isolates utility power from generator power, preventing backfeeding.
- Install a manual or automatic transfer switch.
- Run wiring from the generator to the switch and main panel.
- Connect circuits based on whole-home or essential-load coverage.
5. Fuel System Setup
The fuel connection depends on the generator type and must include proper shut-off and safety components.
- Connect natural gas units to the utility line.
- Install propane lines with regulators and shut-off valves.
- Secure diesel tanks with filtered fuel lines.
6. System Testing and Inspection
Before approval, the system is tested under load and inspected to confirm safe operation.
- Test the generator while powering selected circuits.
- Verify safety systems and monitoring features.
- Complete final inspections and approvals.
Safety Considerations During and After Installation
- Carbon Monoxide Prevention: Always operate generators outdoors and install CO detectors inside the home.
- Proper Grounding: Ground generators according to NEC requirements to reduce shock risks.
- Fuel Storage Safety: Store fuel in approved containers away from heat sources.
- Weather Protection: Use weather-rated enclosures or covers for portable units.
How Much Does Generator Installation Cost?
| Component | Typical Cost |
|---|---|
| Generator Unit (8 to 14 kW) | $3,000 to $4,500 |
| Generator Unit (16 to 22 kW) | $4,500 to $6,500 |
| Generator Unit (24 kW+) | $6,500 to $12,000+ |
| Transfer Switch | $500 to $1,200 |
| Installation Labor | $1,800 to $5,500+ |
| Fuel Tank Installation | $600 to $3,500 |
| Permits and Inspections | $100 to $500 |
| Annual Maintenance | $150 to $450 |
Total Installed Cost: Most whole-home standby systems cost between $8,500 and $23,000, with complex installations exceeding $25,000.
Choosing the Right Installer
Look for professionals who offer experience, transparency, and proper credentials.
- Licenses and Certifications: Electrical, plumbing, and manufacturer training.
- Fuel-Type Experience: Propane, diesel, or natural gas expertise.
- Proof of Insurance: Protection during installation.
- References and Reviews: Recent customer feedback.
- Clear Written Quotes: Itemized pricing for labor, permits, and equipment.

Questions to Ask Your Pro
These questions can help you compare bids and avoid surprises.
- Which generator size do you recommend for my home?
- What fuel type makes the most sense here?
- Will my electrical system need upgrades?
- What type of transfer switch do you recommend?
- Are there local codes or HOA rules I should know about?
- Who handles permits and inspections?
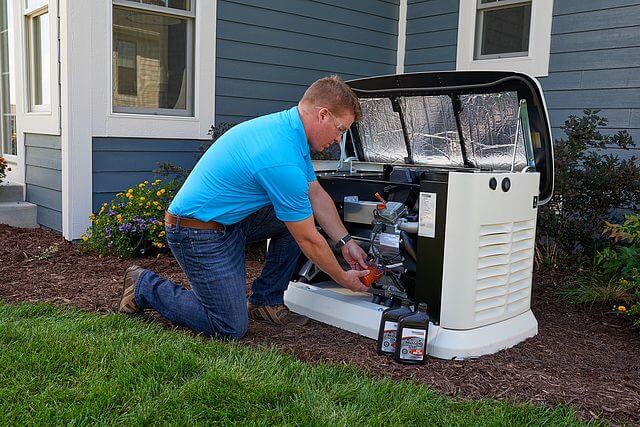
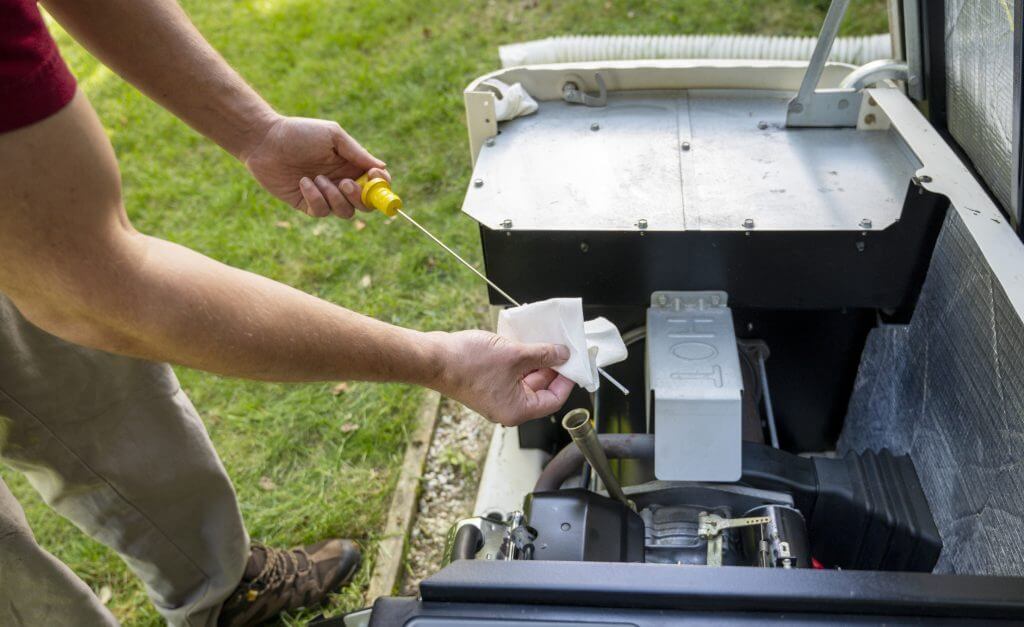
After Installation: Ongoing Care
- Schedule annual maintenance for oil changes and system testing.
- Keep fuel fresh and monitor propane or diesel levels.
- Run the generator monthly under load.
- Inspect for debris, corrosion, or pests.

Final Thoughts
A generator is a valuable investment in your home’s safety and comfort — but only when installed correctly. Portable generators can work well for DIY use, while whole-home standby systems are best left to licensed professionals.
With proper installation and ongoing care, your generator can provide reliable backup power and peace of mind year-round.
Compare top-rated generators pros in your area.
Read real homeowner reviews, explore qualifications, and view promotions. Modernize makes it easy to browse professionals and find one that will be perfect for your project.