Energy-Efficient Windows: What Is ENERGY STAR and How Does It Work?
ENERGY STAR is a voluntary certification program run by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Windows that earn the ENERGY STAR label meet strict performance standards for energy efficiency based on climate-specific criteria.
Not all energy-efficient windows qualify as ENERGY STAR. To earn certification, windows must be independently tested and verified for performance.

Requirements
- Manufactured by an ENERGY STAR partner.
- Tested and certified by the National Fenestration Rating Council (NFRC).
- Meet EPA performance thresholds for:
- U-Factor: How well the window insulates.
- Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC): How much solar heat the window blocks.
- Air Leakage (AL): How much air passes through the window.
- Visible Transmittance (VT): How much natural light enters.
- Condensation Resistance: Ability to resist moisture buildup.
To confirm certification, look for the blue ENERGY STAR label and review the NFRC performance sticker on the window.
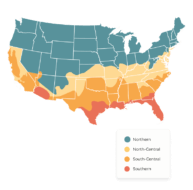
ENERGY STAR Requirements by Region
The ENERGY STAR certification guidelines set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) vary by region to reflect differences in climate and weather patterns. Today, ENERGY STAR divides the country into four climate zones: Northern, North-Central, South-Central, and Southern.
Within each zone, windows must meet specific performance requirements for U-factor and Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC). These ratings ensure windows are optimized for local heating and cooling needs rather than using a one-size-fits-all standard.
| Climate Zone | Primary ENERGY STAR Focus | Typical Performance Targets* |
|---|---|---|
| Northern | Maximum insulation and heat retention | Lower U-factor (around 0.22 or lower); SHGC flexibility for equivalent performance |
| North-Central | Balanced insulation and solar control | U-factor around 0.25 or lower; moderate SHGC limits |
| South-Central | Reduced solar heat gain with solid insulation | Lower SHGC (around 0.28 or lower); moderate U-factor |
| Southern | Strong solar heat blocking | Lowest SHGC (around 0.23 or lower); less restrictive U-factor |
Important note for Northern climates: ENERGY STAR allows multiple performance paths. Certain combinations of U-factor and SHGC provide equivalent energy performance, even if one value is slightly higher or lower than another qualifying option.
Because of these regional differences, a window that qualifies as ENERGY STAR certified in one part of the country may not qualify in another. Always check the ENERGY STAR label and NFRC rating sticker to confirm which climate zones a specific window is approved for.
Energy-Efficient Window Costs
ENERGY STAR windows cost more than standard models, but the efficiency gains can offset the higher upfront price over time.
| Window Type | Average Installed Cost (2026) |
|---|---|
| Vinyl ENERGY STAR Windows | $800 to $1,050 |
| Fiberglass ENERGY STAR Windows | $1,200 to $1,700 |
| Composite ENERGY STAR Windows | $1,300 to $1,900 |
| Wood ENERGY STAR Windows | $1,000 to $1,800+ |
| Triple-Pane ENERGY STAR Windows | $1,200 to $2,200+ |
Most Energy Efficient ENERGY STAR Windows
The most energy-efficient windows combine the right frame material, glass package, and performance ratings for your climate.
Top Window Materials for ENERGY STAR Efficiency
- Fiberglass: Extremely stable, excellent insulation, minimal expansion and contraction.
- Vinyl: Affordable, low maintenance, strong thermal performance.
- Composite: Blended materials that balance durability and insulation.
- Wood (Clad): Natural insulation with protected exteriors.
Top Features for ENERGY STAR Efficiency
- ENERGY STAR Glass: Low-emissivity (Low-E) coatings that reduce heat transfer.
- Multiple Panes: Double- and triple-pane designs improve insulation and noise reduction.
- Gas Fills: Argon or krypton gas between panes improves thermal performance.
- Warm-Edge Spacers: Reduce heat loss around the edges of the glass.
- Tight Air Seals: Low air leakage ratings improve comfort.
Top Energy Efficient Window Brands
See our Best Window Brands guide for a full comparison, or tap the links below to read our brand reviews.
| Brand | ENERGY STAR Highlights | Typical Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Andersen | Fibrex frames, climate-specific glass packages | $800 to $1,600+ |
| Pella | Advanced Low-E glass, multiple certified lines | $750 to $1,700+ |
| Marvin | High-performance fiberglass and composite options | $900 to $2,000+ |
| Simonton | Affordable ENERGY STAR vinyl windows | $700 to $1,100 |
Benefits of ENERGY STAR Windows
In addition to lowering household energy costs, ENERGY STAR windows help reduce overall energy demand and environmental impact.
ENERGY STAR Window Savings
Homeowners can save approximately $100 to $600 per year by upgrading to ENERGY STAR windows, depending on climate, window size, and the efficiency of existing windows.
Homes replacing single-pane windows see the greatest savings.
Environmental Benefits
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions
- Lower overall energy demand
- Improved indoor temperature stability
ENERGY STAR Skylight Windows
ENERGY STAR skylight requirements differ from standard window requirements because skylights are installed at an angle and receive more direct sunlight throughout the day. As a result, ENERGY STAR allows skylights to meet different performance thresholds than vertical windows.
In general, ENERGY STAR–certified skylights are permitted to have a higher U-factor and, in some regions, a higher Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) compared to wall windows. These adjustments account for the unique way skylights gain and lose heat.
Even though ENERGY STAR standards for skylights are more flexible, choosing the right performance ratings is still critical. In colder climates, skylights with a high U-factor can allow significant heat loss, reducing overall energy efficiency. In warmer climates, skylights with a high SHGC can increase cooling costs by allowing excessive solar heat into the home.
ENERGY STAR Skylight Performance by Region
| Climate Zone | ENERGY STAR Focus for Skylights |
|---|---|
| Northern | Lower U-factor to limit heat loss; SHGC flexibility for solar gain |
| North-Central | Balanced insulation and moderate solar control |
| South-Central | Lower SHGC to reduce solar heat gain |
| Southern | Strong solar heat blocking; U-factor is less restrictive |
Because skylight performance has a greater impact on energy use than standard windows, it’s especially important to confirm that the product is ENERGY STAR certified for your specific climate zone and to review the NFRC rating label before installation.
ENERGY STAR Storm Windows
Storm windows can also earn ENERGY STAR certification when they include low-emissivity (Low-E) glass. Like ENERGY STAR–certified replacement windows, these storm windows are designed to reduce heat loss in winter and limit heat gain in summer, helping keep your home more comfortable year round.
According to estimates from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, installing Low-E ENERGY STAR storm windows over existing single-pane windows can save homeowners up to $350 per year on heating and cooling costs. Homes with older, inefficient windows typically see the greatest benefit.
If your home already has standard storm windows, upgrading to ENERGY STAR–certified Low-E storm windows can still improve performance, with average additional savings of around $50 per year.
While storm windows are not a replacement for full window upgrades, they can be a cost-effective energy efficiency improvement for older homes or situations where full replacement is not practical.
 ENERGY STAR Windows Q&A
ENERGY STAR Windows Q&A
Are ENERGY STAR windows worth it?
Yes. For most homeowners, ENERGY STAR windows deliver long-term savings, improved comfort, and better resale appeal.
What is a good ENERGY STAR rating for windows?
A lower U-factor and a climate-appropriate SHGC rating indicate better efficiency.
What is the ENERGY STAR on windows?
The ENERGY STAR label confirms the window meets EPA energy-efficiency standards for your region.
Do ENERGY STAR windows qualify for tax credits?
Many ENERGY STAR windows qualify for federal energy efficiency tax credits in 2026, depending on product ratings and current IRS guidelines.
Is .28 a good U-factor for windows?
A U-factor of .28 is considered efficient, especially for colder climates.
Do ENERGY STAR rebates still exist in 2026?
Yes. Rebates vary by state, utility provider, and program availability.
How much do triple-pane ENERGY STAR certified windows cost?
Triple-pane ENERGY STAR windows typically cost $1,200 to $2,200 or more per window installed.

ENERGY STAR Windows: Next Steps
Choosing ENERGY STAR windows starts with understanding your climate, budget, and performance goals. Comparing certified products and working with a trusted local installer ensures you get the full benefit of your investment.
Modernize can connect you with pre-vetted window professionals who offer ENERGY STAR–certified options and competitive pricing.
Compare top-rated windows pros in your area.
Read real homeowner reviews, explore qualifications, and view promotions. Modernize makes it easy to browse professionals and find one that will be perfect for your project.









